5 GitLab for collaboration
- Know that GitLab, just like GitHub, is a web-based Git repository manager.
- You have learned that GitLab provides features to manage the development process and facilitate collaboration between developers.
- Can use merge requests to propose and review changes before merging them into the main branch.
- You know that issues are a way to manage the development process, track bugs, and discuss new features.
5.1 GitLab
GitLab is a web-based Git repository manager with wiki and issue tracking features.
It is a software that allows to host and manage remote repositories.
In addition, it provides a lot of features to manage the development process and facilitate collaboration between developers.
5.2 Merge requests
When you work in a team, you may want to review the changes before merging them into the main branch.
It is a feature of GitLab to allow are structured comparison of code changes, and comment on them. Often a Merge Request becomes a long thread of comments and discussions about the changes, where multiple developers particpate.
In software development, this is called a “code review” and an integral part of the development process ensuring a good code quality and functionality.
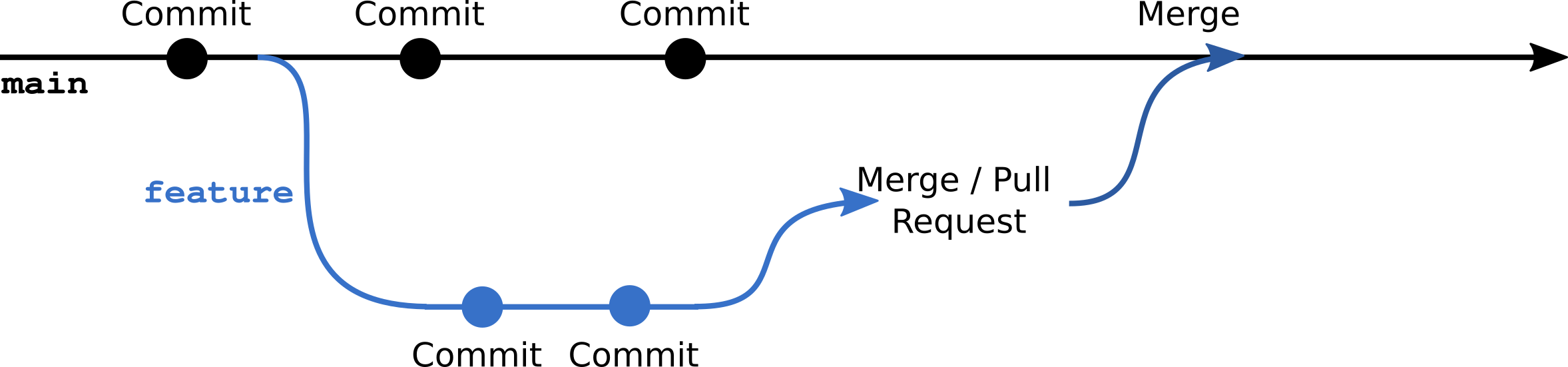
When the code review is concluded, the Merge Request allows merging the changes into the main branch directly on the GitLab platform.
To incorporate the changes in the main branch after merge on your local repository, you need to pull the changes from the remote repository:
git pullIn GitLab, a request to merge changes is called a “Merge Request”. In GitHub, it is called a “Pull Request”. The describe the very same thing. Due to GitHub’s popularity the term “Pull Request”, often abbreviated as “PR”, is more common.
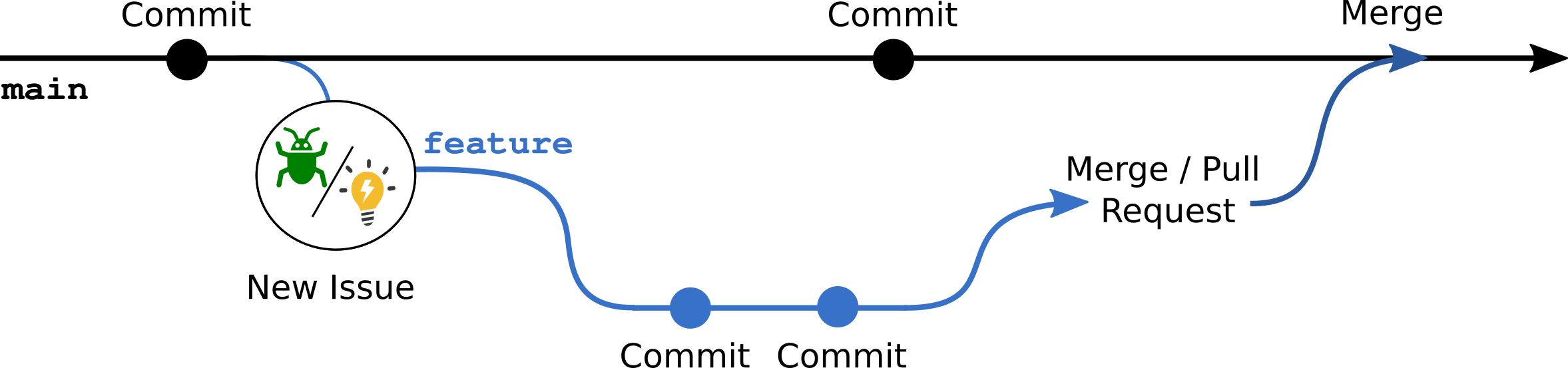
5.3 Issues
The second feature, that is provided by GitLab and GitHub to manage the development process are “Issues”.
Issues are used to track bugs, feature requests, and other tasks.
Similar to merge requests, they can be seen as discussion threads to guide the development process. Also, they can be used important project management to track changes or new ideas.
Issues do not directly interact with the git workflow, but can be used to describe features and can be referred to in feature-branches or pull request.